Classification of Crane Reducers and Their Core Role in Industrial Transmission
In the field of heavy material handling, the crane is indispensable key equipment for achieving efficient operations. The performance and reliability of every crane largely depend on the precise design and manufacturing of its power transmission system, with the crane reducer being the core component of this critical system. Within modern industrial transmission systems, the technological development of these reducers directly affects the efficiency, safety, and lifespan of the entire crane. This article systematically explains the main classifications of crane reducers and analyzes the important role they play in the broader context of industrial transmission systems that support crane operations.

Classification System of Crane Reducers
Based on differences in transmission principles, structural forms, and load-bearing characteristics, crane reducers can be mainly divided into the following categories:
Gear Transmission Reducers
This is the most widely used type of crane reducer, characterized by high efficiency and a compact structure. Common subtypes include:
Cylindrical Gear Reducers: Mature in technology and easy to maintain, commonly used in general-purpose overhead cranes.
Bevel Gear Reducers: Suitable for applications requiring a change in the direction of transmission, such as certain jib cranes.
Planetary Gear Reducers: Offer advantages like high transmission ratios and small size, often found in large port cranes with stringent installation space requirements.
Worm Gear Reducers
This type of reducer relies on the meshing of a worm wheel and worm gear to achieve transmission, featuring smooth operation, low noise, and self-locking capability. It is commonly used in crane applications requiring precise positioning and preventing load slippage, serving as an important solution for safety within industrial transmission.
Special Transmission Reducers
This category includes cycloidal pinwheel reducers and hybrid transmission designs that have emerged in recent years. They are often designed for specific working conditions, such as metallurgical cranes with high impact and frequent start-stop cycles, showcasing the innovations in industrial transmission technology to address engineering challenges.
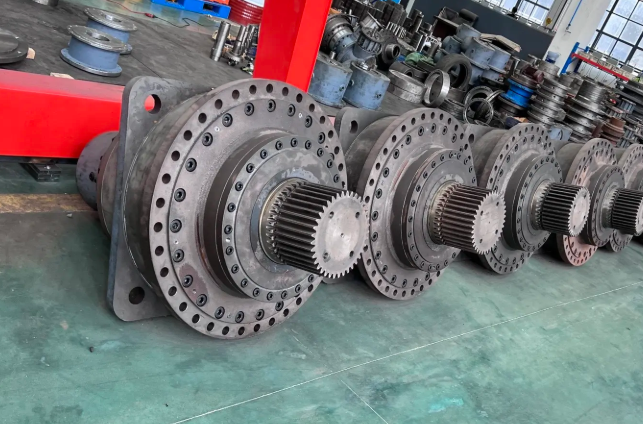
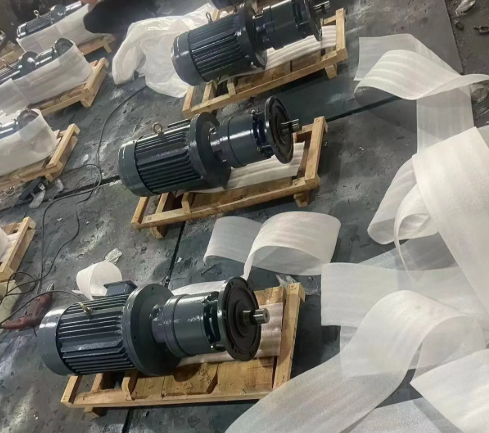


Integration and Function within Industrial Transmission Systems
The crane reducer does not operate in isolation; it is embedded within a complete industrial transmission chain, working in synergy with motors, brakes, couplings, and other components:
Power Matching Hub: The reducer converts the motor's high-speed, low-torque output into the low-speed, high-torque output required for hoisting operations, which is a fundamental requirement for all crane transmissions.
Key Link in Motion Control: Its transmission precision and rigidity directly affect the smooth operation and positioning accuracy of the crane.
Focus for Energy Efficiency Improvement: Advanced reducers reduce internal power loss by optimizing gear design and manufacturing processes, thereby enhancing the energy utilization efficiency of the entire industrial transmission system.
Technological Evolution and Future Trends
With the development of smart manufacturing and green industry, crane reducer technology is undergoing profound changes and driving overall progress in the field of industrial transmission:
Intelligent Integration: Built-in sensors enable real-time monitoring of operating status and predictive maintenance, making crane management more intelligent.
Lightweighting and High Strength: The use of new materials and processes improves reliability and lifespan while reducing weight.
Pursuit of Ultimate Efficiency: Striving for higher transmission efficiency directly reduces the long-term operational energy consumption of cranes.
Systematic Design Thinking: Reducer design increasingly focuses on matching the entire industrial transmission system and crane working conditions, providing customized solutions.
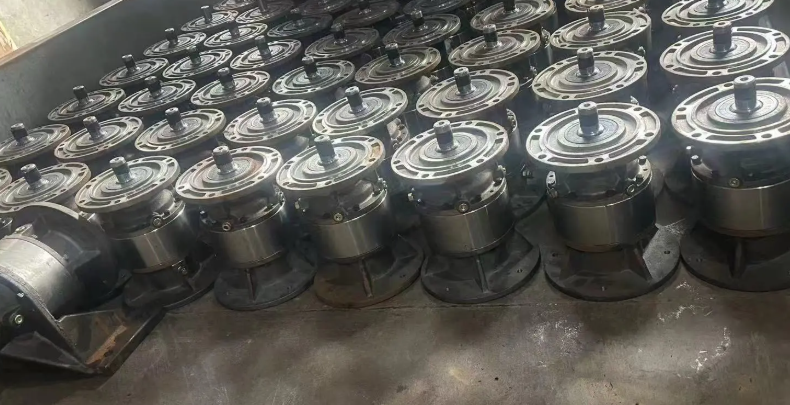
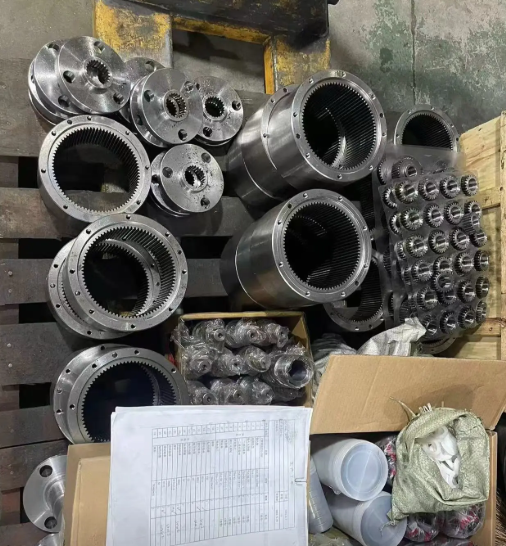


Conclusion
As the power center of the crane, the technological level of the crane reducer is a key indicator of the modernization level of lifting equipment. Within complex industrial transmission systems, correctly selecting and developing suitable reducers not only ensures the safe and efficient operation of the crane but is also a core driving force propelling the entire material handling industry—and crane technology in particular—toward greater reliability, energy efficiency, and intelligence. The advancement of the crane reducer directly supports the evolving performance demands of modern cranes, enabling more precise, durable, and adaptive crane operations across various industrial settings. In the future, continuous technological integration and innovation will undoubtedly drive the co-evolution of the crane, the crane reducer, and the broader industrial transmission system at a deeper level, further solidifying the crane's role as an essential and evolving asset in global industry.

